1. How do snakes unhook their jaws?
Snakes use very elastic tendons to stretch their jaws downwards and the bottom jaw bone is split into two pieces which allows the bottom jaw bone to open up sideways.
If you look under a snakes bottom jaw you will see a line that runs from the center of the lower jaw bone - back towards the throat area. This is were the jaw is split, and the line you see is the skin folded up inside the mouth. The skin stretches to allow the sides of the jaw to open wide when the two parts of the jaw bone are pulled apart.
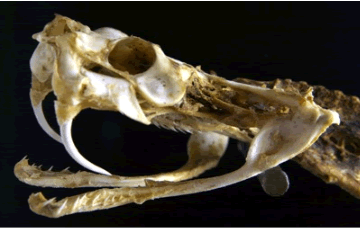
2. Can shakes feel with their tongues?
Jacobs Organ: This is a gland located in the recess of the upper jaw. This organ helps to detect pheromones, scents, and location of prey.
When the snake extends the tongue it gathers scent particles in the air on the 2 forks. When the tongue is withdrawn it touches the 2 groves of the Jacobson's Organ. It is then sent via a nerve to the brain that then tells the snake it is prey, a mate, a predator, etc....
The Jacobson's Organ allows the snake to continue to "breathe" when the snake is swallowing prey much larger than their mouth
(esophagus).

3. Do snakes have ears? Do snakes hear?
Humans have five senses: sight, hearing, taste, touch, and smell.
Animals possess several extra senses, including altered vision and hearing, echolocation, electric and/or magnetic field detection, and extra chemical detection senses. Snakes use their Jacobson's Organ to gather information (sense).
Snakes do not have external ears or eardrum, they do have inner ear structures. A bone called the quadrate bone (in the jaw) moves slightly in response to vibrations. The quadrate bone has been shown to respond to airborne vibrations as well as ground vibrations.
As with other animal ears, this movement is transferred (by bones) to the inner ear, from which signals are sent to the brain and are interpreted as sound. Researchers have determined that snakes are able to detect low frequency airborne vibrations through their inner ears. Snakes also respond to airborne vibrations via the lungs, and to ground vibrations via receptors associated with their belly muscles.

4. Do snakes go blind when they shed their skins?
Snakes do not have eyelids; instead they have specially adapted scales over their eyes called eye caps. These are normally shed along with the skin during each shed cycle, but sometimes they do not shed properly if the snake does not have enough humidity.
The snake does not go blind when it is shedding and the eye are being removed, but it's vision is limited during this time.
5. Why do snakes shed their skin?
Snake skins consist of overlapping scales. Snakes shed the outer layer of their skin as they outgrow the old one, and those that are not growing also shed, replacing their worn scales with a new, healthy skin.
Some snakes shed every few weeks, others shed only about once a year. A new layer develops below the surface of the old skin.
The snake begins the shedding process by rubbing its nose against rocks or other hard objects to start the separation of the old layer from its lips, and then crawls out of its old skin.
The shiny new skin is already developed under the old skin that is shedding off.

6. How are a snakes "babies" born? Where do they lay their eggs? Where do snakes sleep?
The snake will lay her eggs in these safe places. Like other reptiles, most snakes lay eggs (70%).
Although egg-laying snakes appear to just lay ‘em and leave ‘em, all mama snakes care for their babies and are very particular about where they lay their eggs. They search for a spot which is damp and warm, and predator proof. A female may travel long distances to use her regular personal nest site.
Some females, although they don’t coil around their eggs, will stay near the spot where they laid their eggs, keeping away predators.
Snake eggshells are soft leathery parchment-like and not hard like birds’ eggs. So while snake eggshells are permeable, allowing gases to exchange so the embryo can breathe.
Most live-bearing mothers actually retain their eggs. These develop in transparent egg membranes like beads on a string. The embryos are not connected to the mother’s tissues. When the young are ready to "hatch", the mother lays them. Each live young emerges encased in a clear membrane, and have to break out of it by themselves.
All snakes which live in cool climates give birth to live young because laid eggs will not be warm enough to develop properly. Live birth is also common among terrestrial snakes in warmer areas. Tree-dwelling snakes get too heavy carrying eggs and so lay them.
A snake which retains her eggs is looking after them and sacrifices much. The eggs take up body space so she doesn't eat much, if at all. She is also more vulnerable to predators; the eggs make her slow and clumsy, and she exposes herself by actively shuttling between basking and shady spots to ensure an ideal body temperature.
The female King Cobra constructs an elaborate nest. She uses her coils to scrape together leaves, twigs and vegetation, deposits her eggs and covers them with vegetation which generates heat as it decays. She makes another chamber above the nest where she and her mate rest. They actively patrol the area around the nest chasing off predators.
Pythons are among the best egg-laying mamas. They not only coil around their eggs, but if the temperature falls, will “shiver” to raise the body temperature and keep the eggs warm. Their eggs need to stay within a narrow 5 degrees C range in order to develop properly.

7. Why do snakes play dead?
The only snake that "play's dead" is the Hog nose Snake who lives in Mexico and South America. Much like the opossum, the hog nose snake will turn over on his back and pretend to be dead when he is scared.
Most snakes will crawl away or fight back if they are forced to when they are scared.
8. Who are the snake's predator?
Large birds, wild boars, mongooses, raccoons, foxes, coyotes and other snakes are predators of snakes.
Humans hunt snakes for various reasons. Many different breeds of snakes are captured and shipped to other countries to be sold in pet shops. Venomous snakes are used for making anti-venom, which is made from their venom and is used to save the life of a snakebite victim. Snakeskin is used for making many things including shoes, purses and belts. And, unfortunately, many people often kill snakes out of fear.
One of the biggest threats to the snake population, the same as with many other animals, is the destruction of their habitats by humans. Their homes are being destroyed to make room for apartments, buildings, shopping malls, and highways.
9. What do snakes eat?
Snakes are carnivores which means that they eat meat. What type of meat the snake eats depends upon its environment. Snakes that live in the rainforest eat frogs, toads, small birds, mice, and fish.
Larger snakes will eat rabbits, chickens, small mammals, etc... Apollo eats white lab rats.
So what type of meat the snake eats depends on where he lives and the animals that live around him.
10. Links:
Totally 3rd Grade - Animal Classification Song
